A comprehensive map of the human complement system from signaling gateway molecule pages
Published in UCSD Molecule Pages, 2013
The human complement activation takes place through one or more of the well-established pathways (alternative, classical, and lectin) consisting of plasma and membrane-bound proteins. All three pathways converge at the level of C3 and are controlled by regulators. The entire network is considered as a simple recognition and elimination system of host immune-complexes and apoptotic cells and pathogens, and therefore promotes host immune homeostasis. The complement system is also involved in cross-talk with other processes related to coagulation, lipid metabolism and cancer. However, many pathogens counteract complement attack through a range of different mechanisms, such as acquisition of host complement regulators to the surface of pathogen, or secretion of complement inactivation factors. In order to have a holistic view of the entire complement network, we have generated expert-authored and peer-reviewed data on each of the 25 known complement and its associated proteins. We created this network of the human complement system under the umbrella of the UCSD Signaling Gateway project. The Signaling Gateway Molecule Pages database publishes curated data on each protein involved in cellular signaling. Each molecule page (on a given protein) provides a textual description and a structured data which exists in different forms, called functional states, participating in cellular signaling. Furthermore, we export the data to BioPAX, SBML and XML formats.
Figure. Complement activation and cancer. “CMAP: Complement Map Database, Bioinformatics (2013)”. 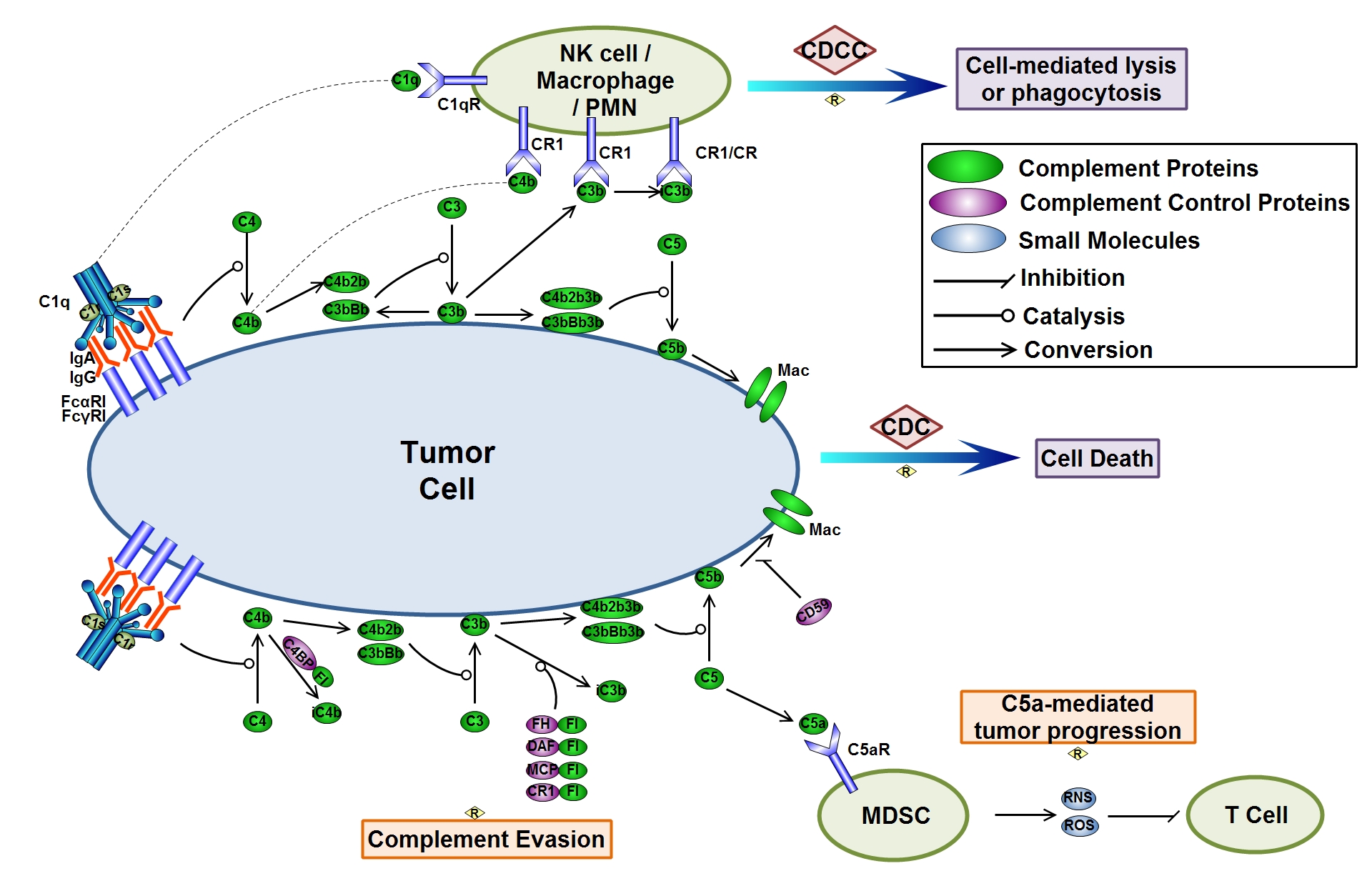
- Dinasarapu AR, A Chandrasekhar, G Hajishengallis, S Subramaniam (2013). Integrin beta-2. UCSD Molecule Pages 2 (2), 33-47. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004263.01
- Dinasarapu AR, A Chandrasekhar, T Fujita, S Subramaniam. (2013) Mannose/mannan-binding lectin. UCSD Molecule Pages 2 (1), 8-18. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004276.01
- Dinasarapu AR, A Chandrasekhar, M Józsi, S Subramaniam. (2013) Complement factor H. UCSD Molecule Pages 1 (2), 71-86. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004256.01
- A Chandrasekhar, Dinasarapu AR, AJ Tenner, S Subramaniam. (2013) Complement C1q subcomponent subunit A. UCSD Molecule Pages 1 (2), 49-60. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004228.01
- A Chandrasekhar, Dinasarapu AR, M Cedzyński, S Subramaniam. (2013) H-Ficolin. UCSD Molecule Pages 2 (2), 26-32. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004267.01
- A Chandrasekhar, Dinasarapu AR, M Matsushita, S Subramaniam. (2013) MAp44. UCSD Molecule Pages 2 (2), 22-25. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A008392.01
- Dinasarapu AR, A Chandrasekhar, J Inal, S Subramaniam (2013). Complement C2. UCSD Molecule Pages 2 (2), 48-53. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004234.01
- A Chandrasekhar, Dinasarapu AR, M Matsushita, S Subramaniam. (2013). MASP-1. UCSD Molecule Pages 2 (2), 10-16. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004274.01
- A Chandrasekhar, Dinasarapu AR, N Thielens, S Subramaniam. (2013). MASP-2. UCSD Molecule Pages 2 (2), 1-9. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004275.01
- A Chandrasekhar, Dinasarapu AR, M Matsushita, S Subramaniam. (2013). MASP-3. UCSD Molecule Pages 2 (2), 17-21. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A008391.01
- A Chandrasekhar, Dinasarapu AR, S Thiel, S Subramaniam. (2013). L-Ficolin. UCSD Molecule Pages 2 (1), 37-44. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004266.01
- A Chandrasekhar, Dinasarapu AR, DE Isenman, S Subramaniam. (2012). Complement C5. UCSD Molecule Pages 1 (2), 61-70. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004240.01
- Dinasarapu AR, A Chandrasekhar, A Sahu, S Subramaniam. (2012). Complement C3. UCSD Molecule Pages 1 (2), 34-48. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004235.01
- J Min, A Chandrasekhar, Dinasarapu AR, C Kemper, S Subramaniam. Properdin. UCSD Molecule Pages. doi:10.6072/H0.MP.A004258.01
